The DeFi sector had a potential $8 billion risk, but only $100 million has exploded so far?
Fund managers, a role once trusted and then demystified in the stock market, carried the wealth dreams of countless retail investors during the A-share boom. Initially, everyone admired fund managers with prestigious university degrees and impressive resumes, believing that funds were less risky and more professional than direct stock trading.
However, when the market falls, investors realize that so-called "professionalism" cannot combat systemic risks. Worse still, they receive management fees and performance bonuses, so if they make money, it's their own skill, but if they lose money, it's the investors' money.
Now, the situation has become even more precarious when the role of "fund manager" has come onto the blockchain under the new name of "Curator" (external manager).
They don't need to pass any qualification exams, undergo any regulatory scrutiny, or even disclose their true identities.
Simply create a "vault" on a DeFi protocol and lure in hundreds of millions of dollars with outrageously high annualized returns. Investors have no idea where this money goes or what it's used for.
$93 million vanished
On November 3, 2025, when Stream Finance suddenly announced the suspension of all deposits and withdrawals, a storm sweeping the DeFi world was pushed to its climax.
The following day, an official statement was released: an external fund manager was liquidated during the sharp market fluctuations on October 11, resulting in a loss of approximately $93 million in fund assets. Stream's internal stablecoin, xUSD, plummeted in response, crashing from $1 to a low of $0.43 within just a few hours.
This storm didn't come without warning. As early as 172 days ago, Schlag, a core developer of Yearn, warned the Stream team. At the eye of the storm, he was even more outspoken:
"Just one conversation with them and five minutes of browsing their Debank account is enough to realize that this is going to end badly."
A conversation between Yearn Finance and Stream Finance
Stream Finance is essentially a yield aggregator DeFi protocol that allows users to deposit funds into vaults managed by so-called Curators to earn yields. The protocol claims to diversify investments across various on-chain and off-chain strategies to generate returns.
This scandal was caused by two main reasons: First, an external Curator used user funds to conduct opaque off-chain transactions, and its positions were liquidated on October 11.
Secondly, on-chain analysts further discovered that Stream Finance also leveraged several times its capital with a small amount of real capital through recursive lending with deUSD in the Elixir protocol. This "left foot stepping on right foot to fly" model, while not the direct cause of the losses, greatly amplified the systemic risk of the protocol and laid the groundwork for the subsequent chain collapse.
These two issues combined to cause a catastrophic chain reaction: $160 million in user funds were frozen, the entire ecosystem faced $285 million in systemic risk, the Euler protocol generated $137 million in bad debt, and $68 million of Elixir's deUSD, which was 65% backed by Stream assets, was hanging by a thread.
So what exactly is this "Curator" model, which seasoned developers can see right through yet still attracts over $8 billion in funding? And how did it gradually push DeFi from a transparent and trustworthy ideal to today's systemic crisis?
The Fatal Transformation of DeFi
To understand the root of this crisis, we must go back to the origins of DeFi.
The core appeal of traditional DeFi protocols like Aave and Compound lies in the principle of "Code is law." Every deposit and every loan must adhere to rules hard-coded into smart contracts, ensuring transparency and immutability. Users deposit funds into a massive public pool, while borrowers must provide substantial collateral to lend money.
The entire process is algorithm-driven, with no human manager intervention. The risks are systemic and calculable, such as smart contract vulnerabilities or liquidation risks under extreme market conditions, but are by no means the human-caused risks of a particular "fund manager".
However, during this period, a new generation of DeFi protocols, represented by Morpho and Euler, implemented a novel fund management approach in pursuit of higher returns. They argued that Aave's public fund pool model was inefficient, with a large amount of funds remaining idle and failing to maximize returns.
Therefore, they introduced the Curator model. Instead of depositing money into a single pool, users choose individual "vaults" managed by the Curator. Users deposit money into the vaults, and the Curator is fully responsible for how to invest and generate interest on that money.
The expansion speed of this model is astonishing. According to DeFiLlama data, as of now, the total value locked in the two major protocols, Morpho and Euler alone, has exceeded $8 billion, with Morpho V1 reaching $7.3 billion and Euler V2 reaching $1.1 billion.
This means that more than $8 billion in real money is being managed by a large number of Curators from diverse backgrounds.
This sounds wonderful: professionals doing what they do best, and users can easily obtain higher returns than Aave. But beneath the glamorous facade of "on-chain finance," its core is actually very similar to P2P lending.
The core risk of P2P lending used to be that ordinary users, as investors, could not judge the true credit and repayment ability of the borrowers on the other end, and the high interest rates promised by the platforms were backed by unfathomable default risks.
The Curator model perfectly replicates this. The protocol itself is just a matchmaking platform. Users' money seems to be invested in professional Curators, but in reality, it is invested in a black box.
For example, on Morpho, users can see various vaults set up by different Curators on its website, each boasting an attractive APY (annualized yield) and a brief strategy description.
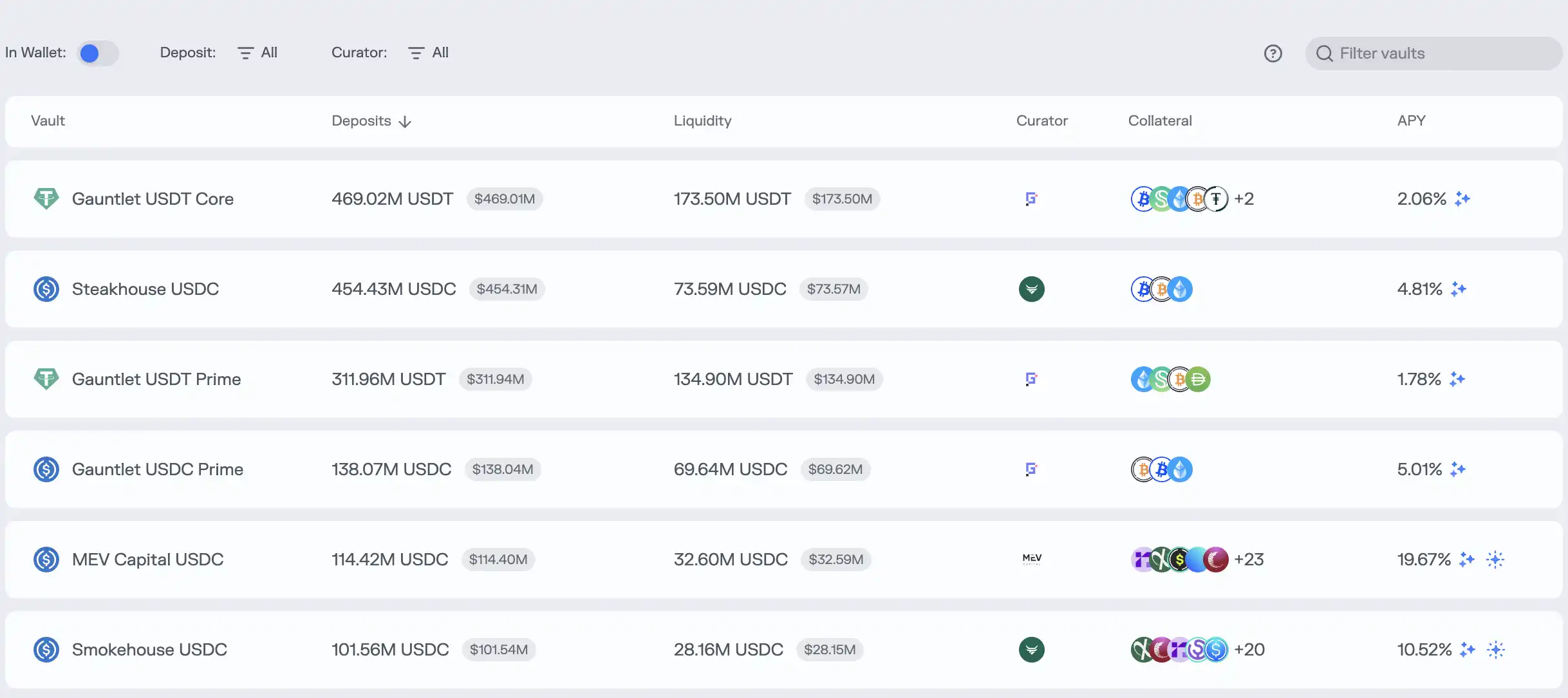 For example, "Gauntlet" and "Steakhouse" in this picture are the curators for the corresponding vaults.
For example, "Gauntlet" and "Steakhouse" in this picture are the curators for the corresponding vaults.
Users can deposit their USDC and other assets simply by clicking "deposit." But that's precisely the problem: aside from the vague strategy description and the constantly fluctuating historical return rates, users often know nothing about the inner workings of the vault.
The core information regarding the vault's risks is hidden in an inconspicuous "Risk" page. Even if a user manages to click on this page, they can only see the vault's specific holdings. Key information determining asset security, such as leverage ratios and risk exposure, remains nowhere to be found.
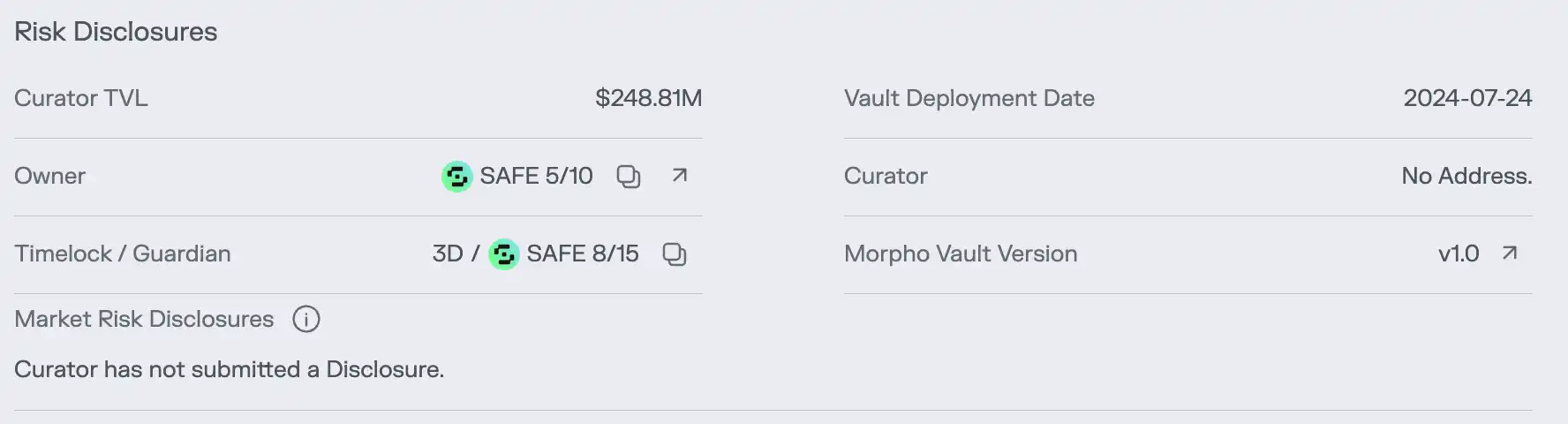 The manager of the vault did not even submit a risk disclosure.
The manager of the vault did not even submit a risk disclosure.  Inexperienced users may find it difficult to assess the security of the interest-bearing assets at the bottom of the vault.
Inexperienced users may find it difficult to assess the security of the interest-bearing assets at the bottom of the vault.
Paul Frambot, CEO of Morpho, once said, "Aave is the bank, and Morpho is the infrastructure of the bank." But the subtext of this statement is that they only provide tools, while the real "banking business," namely risk management and capital allocation, is outsourced to these Curators.
The so-called "decentralization" is limited to the moment of deposit and withdrawal, while the most important risk management link is completely in the hands of an unknown and unrestrained "manager".
It can truly be described as: "Decentralized money transfer, centralized money management."
The reason traditional DeFi protocols are relatively secure is precisely because they minimize the influence of human factors. However, the Curator model of DeFi protocols brings the greatest and most unpredictable risk—human beings—back to the blockchain. When trust replaces code, and transparency becomes a black box, the very foundation of DeFi security collapses.
When the "manager" colludes with the agreement
The Curator pattern merely opened Pandora's box; the tacit collusion between the parties to the agreement and the Curator completely unleashed the demons within.
Curator's profit model typically involves charging management fees and performance-based commissions. This means they have a strong incentive to pursue high-risk, high-return strategies. After all, the principal belongs to the users, and they are not responsible for losses; however, they receive a large portion of the profits if they win.
This incentive mechanism of "internalizing benefits and externalizing risks" is almost tailor-made for moral hazard. As Arthur, the founder of DeFiance Capital, criticized, under this model, Curators have the mentality: "If I mess up, it's your money. If I do well, it's my money."
Even more alarming is that, instead of playing their role as regulators, the protocol providers have become accomplices in this dangerous game. To attract TVL (Total Value Locked) in the fiercely competitive market, they need to use astonishingly high APY (Annualized Yield) to attract users. And these high APYs are precisely created by Curators who employ aggressive strategies.
Therefore, the parties to the agreement not only turn a blind eye to Curator's risky behavior, but also actively cooperate with or encourage them to open high-interest vaults as a marketing gimmick.
Stream Finance is a prime example of this opaque operation. According to on-chain data analysis, Stream claims to have a total value locked (TVL) of up to $500 million, but according to DeFillama data, Stream's TVL peaked at only $200 million.
This means that more than three-fifths of user funds have flowed to unknown off-chain strategies, operated by some mysterious proprietary traders, completely deviating from the transparency that DeFi should have.
The statement released by RE7 Labs, a well-known Curator organization, after the Stream Finance scandal, exposed this entanglement of interests.
They admitted that they had identified "centralized counterparty risk" in Stream's stablecoin xUSD through due diligence before listing it. However, due to "significant user and network demand," they decided to list the asset anyway and set up a separate lending pool for it. In other words, they chose to dance with risk in pursuit of traffic and buzz.
When the agreement itself becomes an advocate and beneficiary of high-risk strategies, the so-called risk review becomes a mere scrap of paper.
Users are no longer seeing genuine risk warnings, but rather an elaborate marketing scam. They are led to believe that the high APY (Average Returns) in the double or triple digits are the magic of DeFi, unaware that behind it lies a trap leading to the abyss.
The collapse of dominoes
On October 11, 2025, the cryptocurrency market experienced a bloodbath. In just 24 hours, nearly $20 billion was liquidated across the network. The liquidity crisis and deep losses brought about by this liquidation are emerging from DeFi.
Analysis on Twitter generally suggests that many Curators of DeFi protocols tend to employ a high-risk off-chain strategy called "Selling Volatility" in pursuit of higher returns.
The essence of this strategy is to gamble on market stability. As long as the market remains calm, they can continue to charge fees and make money. However, once the market fluctuates violently, they are prone to losing everything. The market crash on October 11th became the fuse that detonated this bombshell.
Stream Finance was the first major domino to fall in this disaster. Although the official sources did not disclose the specific strategies employed by Curator that caused the losses, market analysis generally points to high-risk derivatives trading similar to "selling volatility."
However, this was only the beginning of the disaster. Because Stream Finance's tokens, such as xUSD and xBTC, were widely used as collateral and assets in DeFi protocols, its collapse quickly triggered a chain reaction that affected the entire industry.
According to preliminary analysis by DeFi research firm Yields and More, Stream's direct debt exposure is as high as $285 million, revealing a massive risk contagion network: the biggest victim is the Elixir protocol, one of Stream's major lenders, which lent it as much as $68 million in USDC, representing 65% of the total reserves of Elixir's stablecoin deUSD.
RE7 Labs, a former partner, has now become a victim as well. Its vaults on multiple lending protocols face millions of dollars in bad debt risk because they accepted xUSD and Elixir-related assets as collateral.
The wider contagion unfolds through a complex "double-collateralization" path, with Stream's tokens being staked in mainstream lending protocols such as Euler, Silo, and Morpho, which in turn are nested within other protocols. The failure of one node, through this spiderweb-like financial network, rapidly propagates throughout the entire system.
The hidden risks planted by the October 11 liquidation event extend far beyond Stream Finance. As Yields and More warned, "This risk map is still incomplete, and we expect more affected liquidity pools and protocols to be exposed."
Another protocol, Stables Labs, and its stablecoin USDX have recently experienced a similar situation and have been questioned by the community.
Problems with protocols like Stream Finance have exposed the fatal flaws in this new Ce-DeFi (centrally governed decentralized finance) model:
When the agreement lacks transparency and power is excessively concentrated in the hands of a few, the safety of users' funds depends entirely on the integrity of the fund manager, which is extremely risky without regulation and rules.
You are the beneficiary.
From Aave's transparent on-chain banking to Stream Finance's asset management black box, DeFi has undergone a fatal evolution in just a few years.
When the ideal of "decentralization" is distorted into a frenzy of "deregulation," and when the narrative of "professional management" masks the opaque reality of fund operations, what we get is not better finance, but a worse banking industry.
The most profound lesson from this crisis is that we must re-examine the core value of DeFi: transparency is far more important than the decentralized label itself.
An opaque decentralized system is far more dangerous than a regulated centralized system.
Because it lacks both the credibility and legal constraints of a centralized institution, and the open and verifiable checks and balances that a decentralized system should have.
Matt Hougan, chief investment officer of Bitwise, once famously said to all investors in the crypto world: "There is no such thing as a risk-free double-digit return in the market."
For every investor attracted by high APY, before clicking the "deposit" button again, they should ask themselves this question:
Do you really understand where the returns on this investment come from? If you don't, then you are the returns.
You May Also Like

Gold Hits $3,700 as Sprott’s Wong Says Dollar’s Store-of-Value Crown May Slip

SoftBank (SFTBY) Stock; Slight Dip Amid AMD Collaboration on AI Infrastructure
